Recently, cooperating with Professor Jingyue Liu(Arizona State University)from electron microscopy technology group of Energy Research Technology Platform, our group has made great progress in the investigation of CeO2-nanorods structure effect on the stability of gold nanoparticles, which has been published on the Journal of the American Chemical Society in the form of corresponding author.
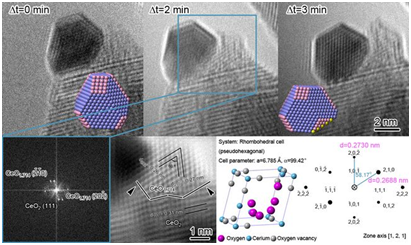
Here, we have reported thatgold particles of 2-4 nm size, strongly anchored onto CeO2-nanorods, are not only highly active but also distinctively stable for the low-temperature water−gas shift reaction. High-resolution TEM (HRTEM) and environmental TEM (ETEM) were used to directly observe the evolutions of the gold-ceria interfaces in the Au/CeO2-nanorods catalyst under oxidizing and reducing atmospheres at 573K, which demonstrated that although the size of gold was not influenced, the morphology of gold was changed, which remained stable under oxidizing atmospheres but gradually restructured under reducing atmospheres. Finally, microstructure of gold particles of 2-4 nm size and chemical function of gold atom located in the surface and interface of Au/CeO2-nanorods was suggested. This work could be extended to develop other types of oxide-supported metal nanoparticles with better stability.
Recently, our group also investigated the structure-dependence studies of morphology and size controlled catalysts. Co3O4-nanorods with well-defined structure has been successfully prepared, whose abundant surface active sites were used for the catalysis of low-temperature CO oxidation(Nature, 458 (2009) 746-749). And via tuning the dehydration mode of the precursor of β-FeOOH with heat treatment of solution, γ-Fe2O3-nanorods of the highest stability was first fabricated, which could effectively active NO and NH3 molecules under rich oxygen atmosphere (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51 (2012) 2989-2993). All these results have great theoretical significance and application value for the preparation of highly active oxide catalysts and also the tuning of metal-oxide interaction
.The research was supported by program of the National Natural Science Foundation and Ministry of Science and Technology of China.